Detailed information about these parameters is presented below.
Unless stated otherwise, this information also applies to the internal
RSJ model (level=1) and the Verilog-A Josephson junction model
provided with WRspice in the Verilog-A examples (level=2).
- level
This specifies the model to use. There are three choices provided in
WRspice. Level 1 (the default) is the internal RSJ model, and
level 2 indicates the Verilog-A example RSJ model, which is available
if it has been loaded. The third choice is level 3, which is an
internal microscopic tunnel junction model described in the next
section.
- pijj
If this flag is given a nonzero integer value, the junctions will be
modeled as a ``pi junction'' meaning that the zero-current phase is
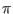 rather than zero. Such devices have been fabricated using
ferromagnetic barrier materials. Although these devices have some
interesting behavior, they are not at this point available or used
with any frequency.
rather than zero. Such devices have been fabricated using
ferromagnetic barrier materials. Although these devices have some
interesting behavior, they are not at this point available or used
with any frequency.
- rtype
The rtype parameter determines the type of quasiparticle branch
modeling employed. Legal values are listed below, only 0 and 1 are
supported in level 2.
| 0 |
The junction is completely unshunted, all shunt conductances
set to zero. |
|---|
| 1 |
Standard model (the default). |
|---|
| 2 |
Analytic exponentially-derived approximation. |
|---|
| 3 |
Fifth order polynomial expansion model. |
|---|
| 4 |
``Temperature'' variation, allow modulation of the gap parameter. |
|---|
Values for rtype larger than 1 are not currently supported in
the Verilog-A model supplied with WRspice in the Verilog-A
examples.
The default is rtype=1. Setting rtype=0 will disable
modeling of the quasiparticle current, effectively setting the shunt
resistance to infinity. Conditions with rtype=1 and 2 are
as described by Jewett, however it is not assumed that the normal
resistance projects through the origin. The icfact parameter
can be set to a value lower than the default BCS theoretical value to
reflect the behavior of most real junctions. The quasiparticle
resistance is approximated with a fifth order polynomial if rtype=3, which seems to give good results for the modeling of some
NbN junctions (which tend to have gently sloping quasiparticle
curves).
Rtype=4 uses a piecewise-linear quasiparticle characteristic
identical to rtype=1, however the gap voltage and critical
current are now proportional to the absolute value of the control
current set with a control=src_name entry in the device
line. This is to facilitate modeling of temperature changes or
nonequilibrium effects. For control current of 1 (Amp) or greater,
the full gap and critical current are used, otherwise they decrease
linearly to zero. If no device control source is specified, the
algorithm reverts to rtype=1. It is expected that a nonlinear
transfer function will be implemented with a controlled source, which
will in turn provide the controlling current to the junction in this
mode. For example, the controlling current can be translated from a
circuit voltage representing temperature with an external nonlinear
source. The functional dependence is in general a complicated
function, but a reasonable approximation is
1 - (T/Tc)4
. See the
examples (A.5) for an example input file (ex10.cir)
which illustrates rtype=4.
It is currently not possible to use other than the piecewise linear
model with this type of temperature variation. If rtype=4, then
legal values for the critical current parameter are cct=0 (no
critical current) and cct=1 (fixed critical current). If
another value is specified for cct, cct reverts to 0.
Thus, magnetic coupling and quasiparticle injection are not
simultaneously available.
- cct
The cct parameter can take one of the following values in level
1, only 0 and 1 are supported in level 2.
| 0 |
No critical current. |
|---|
| 1 |
Fixed critical current. |
|---|
| 2 |
Sin(x)/x modulated supercurrent. |
|---|
| 3 |
Symmetric linear reduction modulation. |
|---|
| 4 |
Asymmetric linear reduction modulation. |
|---|
Values for cct larger than 1 are not currently supported in the
Verilog-A model supplied with WRspice in the Verilog-A examples.
The control instance parameter should be used with devices using
cct 2,3, or 4. With cct=2, the first zero is equal to the
value of the model parameter icon. For cct=3, the maximum
critical current is at control current zero, and it reduces linearly
to zero at control current = 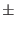 icon
. Junctions with cct=4
have maximum critical current at control current = -
icon, and
linear reduction to zero at control current = +
icon. If cct is specified as 2, 3, or 4, the area parameter, if given, is set
to unity. Otherwise, the model parameters are scaled appropriately by
the area before use.
icon
. Junctions with cct=4
have maximum critical current at control current = -
icon, and
linear reduction to zero at control current = +
icon. If cct is specified as 2, 3, or 4, the area parameter, if given, is set
to unity. Otherwise, the model parameters are scaled appropriately by
the area before use.
- icon
range: 1e-4 - 1.0
Level 1 only.
This parameter applies when the cct parameter is set to one of
the choices larger the 1, where critical current modulation is
modeled. The value of icon is the first value for (assumed)
full suppression of critical current.
The parameter is not currently recognized by the Verilog-A Josephson
junction model provided with WRspice, as that model does not
currently support values of cct larger than 1.
- tc
range: 0.1K - 280K
This is the transition temperature of the material used in the
Josephson junction. We assume that both junction electrodes use the
same material. The default value is 9.26K, the transition temperature
of niobium.
- tdebye
range: 40K - 500K
This is the Debye temperature of the material used in the Josephson
junction. The default is 276K corresponding to niobium. The model
support can compute the superconducting energy gap as a function of
temperature, transition temperature, and Debye temperature using a BCS
expression.
- tnom
range: 0.0K - 0.95*tc
This is the temperature at which all model parameters are measured.
The default is 4.2K, the boiling point of liquid helium.
- deftemp
range: 0.0K - 0.95*tc
This is the default operating temperature of instances of the model,
which can be overridden on a per-instance basis by specifying the
temp_k instance parameter. The default is the tnom
value.
- tcfct
range: 1.5 - 2.5
This is an empirical fitting parameter for approximate temperature
dependence (see 2.17.2.2) of the energy gap, default is 1.74.
- icrit
range: 1nA - 0.1A
This is the critical current of the reference junction at nominal
temperature, which defaults to 1.0mA if not given. This parameter is
not used if cct is 0. the superconducting current through a
Josepjson junctions is
I = Icsin(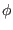 )
)
where Ic
is the critical current. and the junction ``phase'' is
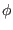 = (2
= (2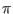 /
/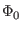 )
)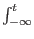 V(t)dt
.
V(t)dt
.
The V(t) is the junction voltage, and 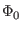 is the magnetic
flux quantum.
is the magnetic
flux quantum.
The icrit parameter should not be confused with the
ics instance parameter. The latter is actually a scale
factor which specifies the instantiated device critical current as
well as appropriately scaling conductances and capacitance, from
the model reference current which is icrit.
- vg or vgap
range: 0.1mV - 10.0mV
This parameter specifies the gap voltage, which in a hysteretic
Josephson junction is a voltage at which there is a large and abrupt
increase in conductivity. This parameter is material dependent. If
not given, the value used is computed using BCS theory from the
operating temperature, superconducting transition temperature, and
Debye temperature, assuming both electrodes are identical.
- delv
range:
0.001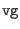 -
0.2
-
0.2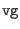
This specifies the assumed width, in voltage, of the quasiparticle
step region, or gap. In this region, current increases sharply with
increasing voltage. The default value of 80uV is reasonable for
high-quality niobium/aluminum oxide Josephson junctions independent of
foundry.
- cap
range: 0.0 - 1nF
This is the capacitance of the reference junction, in farads. This
will override the cpic parameter if given, setting a fixed value
for reference junction capacitance, invariant with icrit. If
not given, junction specific capacitance is set via the cpic
parameter, see below.
- cpic
range: 0.0 - 1e-9
This supplies the default capacitance per critical current in F/A.
This defaults to the MIT Lincoln Laboratory SFQ5EE process <a
href="tolpygo">[Tolpygo]</a> value (0.7pF for 1.0 mA), and will set
the junction capacitance if <tt>cap</tt> is not given. With
<tt>cap</tt> not given, changing <tt>icrit</tt> will change the
assumed capacitance of the reference junction.
- cmu
range: 0.0 - 1.0
This is a new parameter in the current model, which is intended to
account for nonlinearity in scaling of capacitance with area (or
critical current, we actually define ``area'' as the actual over the
reference critical current). It is anticipated that the actual
junction capacitance consists of two components: a physical area
dependent ``bulk'' term, and a perimeter-dependent fringing term. The
cmu is a real number between 0 and 1 where if 0 we assume no
perimeter dependence, and if 1 we assume that all variation scales
with the perimeter. The default value is 0. The capacitance of an
instantiated junctions is as follows:
C = cap(A(1 - cmu) + 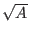 cmu)
cmu)
Here, A
is the ``area'' scaling factor, which is the ratio of the
junction critical current to the reference critical current.
- vm
range: 8mV - 100mV
This is the product of the reference subgap resistance and the
reference device critical current. This parameter is commonly
provided by foundries, and is a standard indicator for junction
quality (higher is better). Values tend to decrease with increasing
critical current density. This defaults to the value for the MIT
Lincoln Laboratory SFQ5EE process[16], which is 16.5mV, The
reference junction subgap resistance is obtained from the value of
this parameter and the critical current, unless given explicitly.
- rsub or r0
range: 8mV/icrit - 100mV/icrit
The reference junction subgap resistance can be given directly
with this parameter, and a given value will override the
vm value if also given.
- icrn
range: 1.5mV - 1.9mV
This is the product of the reference junction ``normal state''
resistance and the critical current, where the normal state resistance
is the differential resistance measured well above the gap. The
default value is that provided for the MIT Lincoln Laboratory SFQ5EE
process[16] which is 1.65mV. This too is a commonly given
parameter from Josephson foundries for characterizing junctions. If
not specified explicitly, this provides the reference junction normal
state resistance from the critical current.
- rnorm or rn
range: 1.5mV/icrit - 1.9mV/icrit
The reference junction normal state resistance can be given explicitly
with this parameter, which will override icrn if this is also
given.
- gmu
range: 0.0 - 1.0
This is analogous to cmu, and applies to the subgap and normal
conductances. The vm, in particular, may vary with junction
physical size, with small junctions having lower vm than larger
ones. This parameter should capture this effect. It is taken that a
significant part of the conductivity is due to defects or
imperfections around the periphery of the junction area, and the
contribution would therefor scale with the perimeter. The scaling for
conductivity is as follows:
Gx = Gx0(A(1 - gmu) + 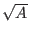 gmu)
gmu)
Here, Gx
refers to either the subgap or normal conductance,
Gx0
is the same parameter for the reference junction. The A
is
the scaling parameter, that is, the ratio of instance to reference
critical currents. The default value is 0, meaning that scaling is
assumed purely linear, which will be the case until a number is
provided through additional data analysis. It may prove necessary to
have separate scaling parameters for subgap and above gap condutance,
at which time a new model parameter may be added.
- icfct or icfact
range: 0.5 - 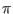 /4
/4
This parameter sets the ratio of the critical current to the
quasiparticle step height. Theory provides the default value of
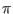 /4
which is usually adequately close. Characterization of
fabricated junctions would provide an improved number.
/4
which is usually adequately close. Characterization of
fabricated junctions would provide an improved number.
- force
range: 0 or 1
If this flag is set, then the only range test applied to subgap and
above gap resistance values is that they be larger than zero. This
affects the parameters that set the quasiparticle branch conductance
values, any input other than a short circuit is allowed.
- vshunt
range: 0.0 - nominal gap voltage
This parameter is unique in that it does not describe an as-fabricated
junction characteristic. Rather, it is for convenience in specifying
a shunt resistance to use globally in SFQ circuits, If given (in
volts) conductance will be added automatically so that the product of
the total subgap conductance and the critical current will equal vshunt. This avoids having to calculate the value of and add an
explicit resistor across each Josephson junction, as used for damping
in these circuits. The designer should choose a value consistent with
the process parameters and the amount of damping required. Higher
values will provide less damping, usually critical damping is desired.
This parameter defaults to 0, meaning that no additional demping is
supplied by default.
- lsh0
range: 0.0 - 2.0pH
- lsh1
range: 0.0 - 10.0pH/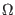
These parameters specify series parasitic inductance in the external
shunt resistor. the vshunt parameter must be given a value such
that the added external conductance is positive, or these parameters
are ignored. The inductance consists of a constant part (lsh0)
assumed to come from resistor contacts, plus a value (lsh1)
proportional to the resistance in ohms, intended to capture the length
dependence.
- tsfactor
range: 0.001 - 1.0
This is mainly for compatibility with the Verilog-A Josephson junction
model provided with WRspice in the Verilog-A examples. This is
equivalent to the WRspice dphimax parameter, but is
normalized to 2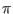 . If not given, it defaults to
. If not given, it defaults to
 /2
/2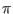 in WRspice, or 0.1 in the Verilog-A model not used in WRspice.
This is the maximum phase change allowed between internal time points.
in WRspice, or 0.1 in the Verilog-A model not used in WRspice.
This is the maximum phase change allowed between internal time points.
- tsaccel
range: 1.0 - 100.0
Time step limiting is performed relative to the Josephson frequency of
the instantaneous absolute junction voltage or the dropback voltage,
whichever is larger. The phase change is limited by tsfactor,
thus corresponding to a maximum time step relative to the period of
the frequency corresponding to the voltage. Note that in SFQ
circuits, where the junctions are critically damped, the junction
voltage is unlikely to exceed the dropback voltage, which is
numerically equal to the critical current times the shunt resistance
(vshunt). This implies that the maximum time step is a fixed
value by default.
When simulating SFQ circuits, between SFQ pulses there is often
significant time where signals are quiescent and one could probably
take larger time steps, speeding simulation. This appears true to an
extent, however one can see signs of instability if steps are too
large.
The tsaccel parameter is the ratio of the longest time step
allowed to that allowed at the dropback voltage. In computing the
time step, the low voltage threshold is reduced to the dropback
voltage divided by tsaccel, so time steps will be inversely
proportional to voltages above this value.
Experimentation suggests that a value of 2.5 is a good choice for RSFQ
circuits, your results may vary.
- vdp (read only)
This parameter returns the computed value of the dropback voltage,
which is the voltage at which the return trace of a hysteretic
Josephson junction i-v curve snaps back to the zero-voltage state. If
is also the voltage equivalent of the plasma resonance, and the
product of critical current and shunt resistance for critical damping.